Glossary of Usenet Terminologies
Last Updated: Oct 01, 2023
We know that Usenet can be quite confusing especially for new users out there. It is a complex system that has quite a few words and technical terms that may not be understandable to a lot of people. That is why UsenetReviewz compiled a list of terminologies to help you, hopefully, understand some of these Usenet-related words or abbreviations better.

A
alt
the hierarchy containing newsgroups devoted to a variety of miscellaneous topics which are mostly unregulated. For example, alt.zines is for discussing small press publications, magazines and pamphlets. Thealt hierarchy is not included in the Big-8 and was created separately as a place with more freedom and fewer rules.
alternative hierarchies
five other Usenet hierarchies not included in the Big 8. These hierarchies are subject to the same approval process as far as creation of a new group Is concerned. However, unmoderated newsgroups within the alternative hierarchies suffer from a great deal of spam. Thefive alternative hierarchies include bionet, bit, biz, k12, alt. Alternative hierarchies should not be confused with the alt hierarchy.
archive
a single file that contains a collection of multiple compressed files created to make the downloading process simpler and faster. Downloaded archives must be unpacked.
article
a Usenet term that means a message sent to a discussion group. Same as posting.
ASCII
An acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, a character encoding standard for electronic communication.
B
Bandwidth
A measure of the volume of data that can be transmitted over a connection in a given time. Often used in the context of download or upload speeds.
backbone
refers to the main pipes that internet data travels on from one network to another.

Big-8
a group ofnewsgroup hierarchies distributed around the world. These hierarchies are managed by the Big 8 Management Group and are subject to well-defined procedures for the creation of new newsgroups. These are the mainstream hierarchies: comp, humanities, misc, news, rec, sci, soc and talk.
binary/ binary file
a file that contains binary data.
binary data
any data that is not text
binary system
a mathematical system used by computer scientists and programmers to work with computer memory.
bit
basic unit of information in computing and digital communications; smallest unit of data storage. In 1 byte, there are 8 bits.
bits per second
unit of measurement used to describe the speed of an internet connection. Abbreviated as bps.
body
refers to the main part of a Usenet article or the text of the article.
byte
unit of data storage consisting of 8 bits.
C
client
a program that requests a service of some type, usually over a network. A program that provides such services is called a server. With Usenet, the client is called a newsreader and the server is called a news server.
comp
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containingnewsgroups discussing computer-related topics. Ex. comp.software.
completion
is a measure of the number of articles a server is storing. Completion is usually expressed in percentage form representing the number of articles stored divided by an estimated total number of available articles. Please note that completion rates are usually just estimates.
completion rate
same as completion
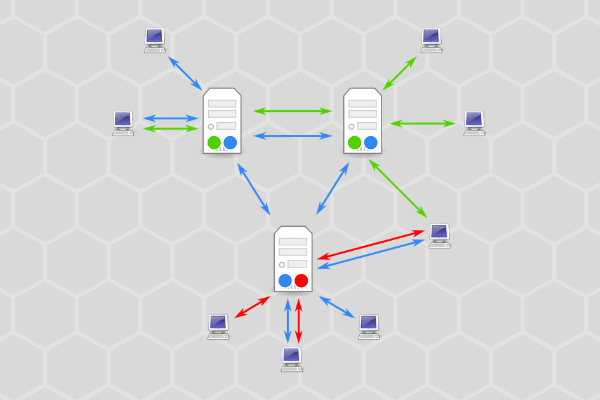
connection
the communication link between a news server and a Usenet client (newsreader). Usenet providers allow multiple connections at the same time for faster downloading. Please note, however, that fast downloads also rely on how fast your own internet connection is.
control message
A short message with a special header line that acts as an instruction to a news server. A control message tells the server to perform a specific task, for example, to create a new newsgroup, remove an existing group, or delete a specific message.
cross-post
to post an article to more than one newsgroup
D
data
refers to binary or text data
date
Within the header of an article, this is the line that contains the time and date an article is posted.
download
to copy a file from one computer to your computer.
E
encrypted Usenet access
takes advantage of SSL technology to encrypt all of the data transmitted between client and Usenet server.
expire
to delete an article after it has been stored in a news server for a particular amount of time. The time after which the article expires is called its retention.
F

FAQ
frequently asked questions list. A list of questions and answers about a particular Usenet topic. Most Usenet providers and newsgroups have FAQs written for new users or newcomers to a particular group.
flame
to attack another Usenet user in a post
follow-up
an article that was written in reply to a previous article.
From
within the header of an article; it is the line that contains the name and address of a person who posted the article.
G
GB
abbreviation for gigabyte
gigabyte
A unit of measurement used for computer memory and data storage. A gigabyte is about 1 billion bytes. Abbreviated as GB.
group
same as newsgroup; a Usenet discussion group.
H
header
a standard section at the beginning of every message that contains technical information in the form of individual header lines.
header line
a single line within the header of a Usenet article. Includes From, newsgroups, subject, data, organization and lines.
hierarchy
categories into which newsgroups are organized. The first part of a newsgroup name shows the hierarchy to which the newsgroup belongs. For example sci.physics is in the sci hierarchy.
humanities
name of one of the Big-8 hierarchy containing topics related to humanities like literature, music and fine arts.
I
IHAVE
a type of Usenet feed used by Usenet servers to exchange articles
incomplete
Describes a multipart binary file for which all the data has not been downloaded. The parchive system was created to enable users to deal with incomplete files by recovering the missing data.

Internet
a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities, consisting of interconnected networks using standardized communication protocols
ISP
abbreviation for Internet Service Provider
J
JPEG
“Joing Photographic Experts Group”. same as jpg
JPG
a file format commonly used to store photographs.
K
KB
Abbreviation for kilobyte
kill file
special file used by newsreaders to indicate that an article is to be discarded automatically. The exact format of a kill file depends on the specific newsreader. You can use a kill file to tell your newsreader to never show you a specified article.
kilobyte
unit of measurement used for computer memory and data storage. A kilobyte is about 1000 bytes. Abbreviated as KB.
L
lines
within the header of an article; line that shows the number of lines in a message not including the header.
M
mainstream hierarchies
also known as the Big-8 hierarchies. The most important Usenet hierarchies distributed around the world that are subject to nomination, discussion and voting. Mainstream hierarchies include comp, humanities, misc, news, rec, sci, soc and talk. Not to be confused with alternative hierarchies.
MB
abbreviation for megabyte
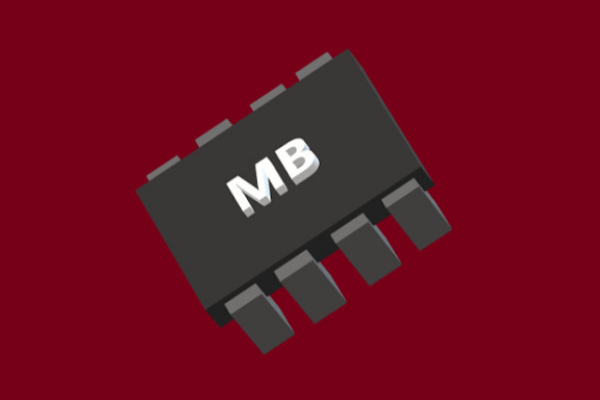
megabyte
unit of measurement used for computer memory and data storage. A megabyte is about 1 million bytes. Abbreviated as MB.
metered Usenet account
an account that is limited to a set amount of monthly bandwidth allowance.
misc
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containingnewsgroups discussing topics that may not be related to the other hierarchies. Ex. misc.kids, misc.education
MIME
(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): An extension of the standard email format allowing non-text data to be sent via email, often used in Usenet for sending binaries.
moderator
a person who controls which articles can or cannot be posted to a specific newsgroup. A newsgroup which is monitored and controlled is said to be moderated.
multipart binary
a binary file broken into multiple parts, each of which is posted separately. The various parts of a multipart binary are gathered and reassembled back into the original file when downloaded.
N
newbie
a new newsgroup user
news
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containing newsgroup-related matters. It is meant to deal with matters of Usenet in particular. Ex. news.admin; news.newusers.questions
news feed
service offered by a Usenet news server. Used as a synonym for news server or NNTP server
news server
server that stores Usenet articles and files and makes them available via a newsreader. Also known as NNTP server
newsgroup
a Usenet discussion group
Newsgroups
in terms of header lines, it is the line that contains the name/s of newsgroups to which the article is posted.
newsreader
a program used to access Usenet
NFO file
a small text file containing information about another larger posting. NFO files can be read with any text editor. An NFO file is often posted along with a multipart binary file in order to describe the contents of the binary.
NNTP
abbreviation for Network News Transfer Protocol. It is used to distribute Usenet articles
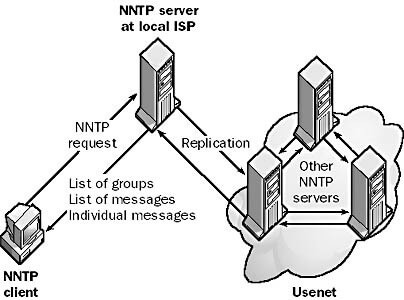
NNTP server
same as news server
NZB file
a file that holds the output of a Usenet search engine or an NZB site. Information in an NZB file is stored in XML format
O
Organization
within the header line, it contains the name of the organization from which the article was sent.
P
PAR file
an old file format used for parity files by the parchive system. PAR files were replaced by PAR2 files

PAR2 file
a file format used for parity files by the parchive system.
parchive
abbreviation for Parity Archive Volume Set. A system used to enhance the reliability of posting and downloading multipart binaries. When a multipart binary file is posted, a number of special parity files are also posted. At the receiving end, if some of the data is not received or is incorrect, the parity files can be used to recover the missing data and create a complete binary file identical to the original. The most widely used program for managing PAR2 files is QuickPar
Peering
The mutual agreement between Usenet providers to exchange data directly, often to increase speed and reliability.
post
to send an article to a Usenet newsgroup
posting
a message sent to a discussion group. Same as an article
Propagation
The time it takes for a Usenet post to be distributed to all servers worldwide.
protocol
set of technical rules used by client and server programs to communicate to one another. In terms of Usenet clients and servers, the protocol used is NNTP.
Proxy Server
An intermediary server that sits between a user’s device and the internet. It intercepts requests from users to make them on their behalf, often used for anonymity or to bypass regional restrictions.
Q
QuickPar
a program used to create and manage parity files in PAR2 format.
quote
to include all or part of an original Usenet article within a reply
R
RAR file
The file format most widely used to distribute multipart binaries on Usenet. RAR files are archives that act as containers, storing one of more files in compressed form. Once a RAR file is downloaded, it must be unpacked in order to be used. If the RAR file is large enough to be posted as a multipart binary, the various parts must be assembled before the RAR file can be unpacked. The most common program used to create and unpack RAR files is WinRAR.
rec
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containing newsgroups dedicated to recreation, hobbies, arts, and entertainment. Ex. rec.art.poetry; rec.music

retention
the amount of time for which the server keeps data. Retention is measured in days. This covers both text and binary data.
RFD
a proposal that initiates the discussion as to whether or not to create new newgroups. An RFD is required to have a newsgroup name, checkgroup file entry and moderated or unmoderated status.
retention rate
same as retention
S
sci
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containing newsgroups dedicated to science-related discussions. Ex. sci.physics; sci.research
search engine
program used to search a large database for specific information
secure connection
a facility used to transmit data sent as encrypted and decrypted as it is received. See also SSL
server
program that offers a service of some type, usually over a network. A program that requests such services is called a client. The term “server” is also used to refer to the computer upon which the server program is running. With Usenet, the server is called a news server, and the client is called a newsreader
session
communication link between a newsreader and a news server. Same as connection
soc
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containing newsgroups dedicated to social and cultural discussions. For example: soc.feminism, soc.culture.African
spam
Unsolicited advertisements or inappropriate messages posted to a Usenet newsgroup
spammer
a person or company that sends spam
SSL
abbreviation for Secure Socket Layer. It is a protocol used to secure connection over the Internet.
Subject
line within the header of an article that contains the subject of the article.
subscribe
To indicate to your newsreader that it should add a specific newsgroup to the list of groups you want to read.
T
talk
one of the Big-8 hierarchies containing newsgroups dedicated to controversial topics with no obvious categorization. Ex. talk.politics; talk.environment
TB
abbreviation for terabyte
terabyte
unit of measurement used for computer memory and data storage. A terabyte is about a trillion bytes.
text
data consisting of characters such as letters, numbers, punctuation and so on.
text file
a file that contains text
TCP/IP
family of protocols used to run the Internet
thread
A sequence of related articles consisting of an original article, and all subsequent replies to that article or to other replies.
troll
a Usenet user who maliciously attacks other Usenet users to start an argument.
U
unlimited Usenet account
an account that offers unlimited downloads without any monthly bandwidth limits.
unsubscribe
To indicate to your newsreader that it should remove a specific newsgroup from the list of groups you want to read.
unzip
to unpack a zip file
upload
to copy a file from your computer to another
Usenet
a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. Usenet has over a hundred thousand different groups and millions of participants around the world.
Usenet provider
a company that provides people with access to a Usenet server. Usenet providers charge a monthly fee for their service
Usenet search engine
A service that searches through Usenet newsgroups to find specific content. Most often they are used to search for binary files.
Uuencoding
abbreviation Unix to Unix encoding. It is a system used to encode binary data as text, suitable for posting within a Usenet article, and then decoding the data back into the original text.
V
volume
a measure of the average number of articles sent to a mailing list.
VPN
abbreviation for virtual private network; a VPN connection establishes a secure connection between you and the internet. By using a VPN, all your data traffic is routed through an encrypted virtual tunnel and disguises your IP address when you use the internet.
W
WinRAR
A widely used program that creates and manages compressed archives in RAR format. WinRAR is available for all popular operating systems.
X
XML
abbreviation for Extensible Markup Language; A general-purpose specification used to transport and store data. The results of a Usenet search engine are typically stored in an NZB file in XML format.
Y
yEnc
system used to encode binary data as text, suitable for posting within a Usenet article, and then decoding the data back into the original text.
Z
zip file
A file or archive (set of files) that is compressed using the “zip” format. Zip files have an extension of zip and must be unpacked by a special program called a zip file program.







